TADOConnection encapsulates the ADO connection object. Use TADOConnection for connecting to ADO data stores. The connection provided by a single TADOConnection component can be shared by multiple ADO command and dataset components through their Connection properties.
Create an Access database and table Using ADOX:
function CreateAccessDatabase(aFileName: string): string;
var cat: OLEVariant;
begin
Result:= '';
try
cat:= CreateOleObject('ADOX.Catalog');
cat.Create('Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=' + aFileName + ';');
cat:= NULL;
except
writeln(ExceptionToString(ExceptionType, ExceptionParam));
writeln('ADOX.Catalog create failed ');
//on e: Exception do Result := e.message;
end;
end;
You call the Create with
Const MYPATH2 ='C:\maXbox\mX47464\maxbox4\examples\maxbase4runtimedb6.mdb';
CreateAccessDatabase(MYPATH2)
ADOX is an extension to ADO that lets you create and modify database structures (tables and fields). It was created specifically for working with the Jet database engine. According to Microsoft, you might have problems using it with other database engines.
Now we create a table with ADO Connect and SQL:
Const MyPath2 ='C:\maXbox\mX47464\maxbox4\examples\maxbase4runtimedb6.mdb';
procedure CreateAccessTable(Sender: TObject;
ADOConnection11: TADOConnection; ADOCommand11: TADOCommand);
var MYDb: TADOConnection;
ADOCommand1: TADOCommand;
begin
MyDb:= TADOConnection.Create(Self);
MyDb.Close;
//Provider=MSDASQL.1;Persist Security Info=False;Data Source=database3
MyDb.ConnectionString:= 'Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;' +
'Data Source=' + MyPath2 + ';' +
'Persist Security Info=True;';
MyDb.LoginPrompt:=False;
MyDb.Connected:= True;
MyDb.BeginTrans;
ADOCommand1:= TADOCommand.create(self)
try
ADOCommand1.connection:= MyDb;
ADOCommand1.CommandText:= 'CREATE TABLE TABLE1 ('
+'ID AUTOINCREMENT,'
+'FirstName varchar(255) NOT NULL,'
+'LastName varchar(255),'
+'Age int )';
ADOCommand1.Execute;
MyDb.CommitTrans;
ADOCommand1.Free;
except
MyDb.RollbackTrans;
writeln(ExceptionToString(ExceptionType, ExceptionParam));
//Exception: Syntax error in CONSTRAINT clause
ShowmessageBig('CREATE Table Exception');
end;
end;
TADOConnection allows you to control the attributes and conditions of a connection to a data store. Use the properties of TADOConnection to control such attributes as record locking scheme (optimistic versus pessimistic), cursor type, cursor location, isolation level, and connection time-out. Methods are also provided for implementing transactions and retrieving metadata about the database to which this component connects.
However, it is useful for creating tables and fields because you can easily define data types and indexes (which you cannot do in ADO).
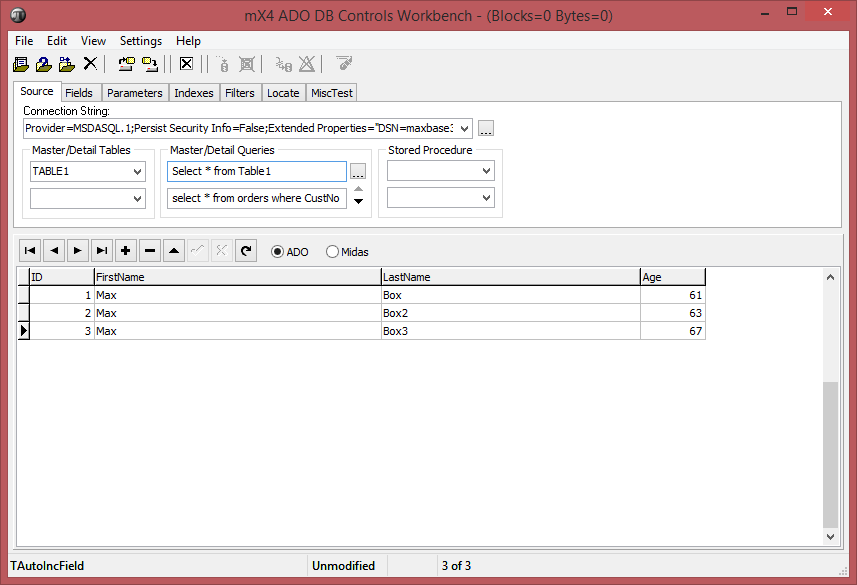
At least we fill the table with a few records and do a Query to show the result:
procedure InsertADORecordClick(Sender: TObject;
ADOConnection1: TADOConnection; ADOCommand1: TADOCommand);
begin
ADOConnection1.BeginTrans;
ADOCommand1:= TADOCommand.create(self)
try
ADOCommand1.connection:= ADOConnection1;
ADOCommand1.CommandText:= 'INSERT INTO Table1 (FirstName, LastName, Age) '
+'VALUES (''Max'',''Box4'', 69)';
ADOCommand1.Execute;
ADOConnection1.CommitTrans;
ADOCommand1.Free;
except
ADOConnection1.RollbackTrans;
writeln(ExceptionToString(ExceptionType, ExceptionParam));
ShowmessageBig('INSERT Exception');
end;
end;
procedure QueryADOSet(AdoConnection: TAdoConnection);
var AdoQuery: TADOQuery;
begin
AdoQuery:= TADOQuery.Create(nil);
try
AdoQuery.Connection:=AdoConnection;
AdoQuery.SQL.Add('SELECT * FROM Table1');
AdoQuery.Open;
while not AdoQuery.EOF do begin
//Writeln(AdoQuery.FieldByname('LastName').AsString);
Write(AdoQuery.Fields[2].AsString+': ');
AdoQuery.Next;
end;
finally
AdoQuery.Free;
end;
end;
In the end we can test it on the SQL ADO Workbench integrated as add-on in maXbox:

ADOX (ADO Extensions for DDL and Security): ADOX refers to ‘ActiveX Data Objects Extensions for Data Definition Language and Security’, and it is an extension to the ADO library in which additional objects, for creating and modifying database tables, and for security, are exposed. To use ADOX in your VBA project, you must add a reference to the ADOX Object Library in Excel (your host application) by clicking Tools-References in VBE, and then choose an appropriate version viz. Microsoft ADO Ext. x.x for DDL and Security. Note that ADO does not by itself support creating databases & tables, which is actually done with ADOX. However, you can create a database table in ADO using SQL. The ADOX Library gives access to objects, properties and methods to create, modify, and view the database and tables structure.
LikeLike